


Typsichere Format-Strings
Ein Beitrag zur Rehabilitierung von printf.
- printf() in C
- Die C++-Alternative: Streams
- CbdeFormat: printf() typsicher
- Beispiel 1: Migration nach C++Builder 2009/Unicode
- Beispiel 2: Debuggen komplizierterer Format-Strings
- Referenzen
- Kommentare
printf() in C
printf()PHP, Delphi, C#/.NET oder Java.Jedoch hat printf()printf()zum Einschleusen von Fremdcode
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void foo (const char* arg)
{
char buf[200];
/* Korrumpiert den Stack, wenn strlen (arg) > 192.
*/
sprintf (buf, "arg: '%s'", arg);
/* Korrumpiert den Stack, wenn der Benutzer mehr als 200 Zeichen eingibt.
*/
scanf ("%s\n", buf);
}Die C++-Alternative: Streams
variable Anzahl von Stackargumenteneinen oder anderenIO-Streamsprintf()printf()printf(): man kann dank ADLDas Problem ist nur:konzisen Beispieles von C nach C++:int iVal = 2;
int hVal = 0x0C;
const char* filename = "test.fil";
const char* username = "juser";
float fValue = 23.8;
// C
#include <stdio.h>
void doItWithPrintf (void)
{
printf ("%4d 0x%02X Testfile: [%10s] user: [%-10s]\nTrial %8.2f \n",
iVal, hVal, filename, username, fValue);
}
// C++
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
int doItWithIOStreams (void)
{
cout << setw(4) << iVal;
cout << " 0x" << hex << uppercase << setprecision (2) << setfill ('0') << setw (2) << hVal;
cout << setfill (' ') << dec; // reset things
cout << " Testfile: [" << setw (10) << filename << "]";
cout << " user: [" << setw (10) << left << username << right << "]";
cout << "\n";
cout << "Trial " << setw (8) << fixed << setprecision (2) << fValue;
cout << endl;
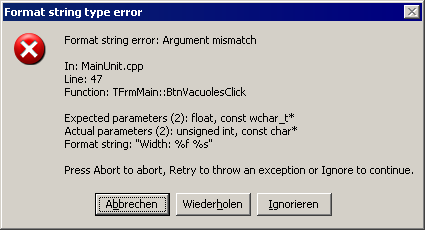
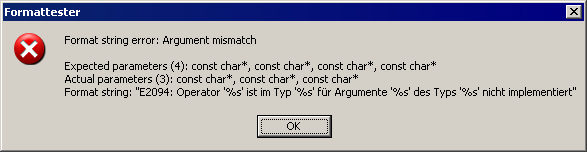
}void e2094 (const char* op, const char* lhstype, const char* rhstype)
{
// C-Variante
std::fprintf (stderr, gettext ("E2094: Operator '%s' not implemented in "
"type '%s' for arguments of type '%s'"),
op, lhstype, rhstype);
// C++-Variante
std::cerr << gettext ("E2094: Operator '") << op
<< gettext ("' not implemented in type '") << lhstype
<< gettext ("' for arguments of type '") << rhstype
<< '\'' << std::endl;
}CbdeFormat: printf() typsicher
Mit boost::format()sprintf() zu beseitigen:
- keine Anpassungen notwendig.
- geringen Laufzeit-Overhead
- Concepts
- CbdeFormat verwaltet eine (beliebig erweiterbare) Liste von Funktionen wie printf(), sprintf(), scanf()
- Code Completion und Parameter Insight funktionieren innerhalb von Makro-Aufrufen nicht.
Die Bibliothek kann in der C++Builder
- Da es in C++ noch keine Variadic TemplatesVariant::OleProcedure()formatgen erzeugt der Installer anhand einer Parameterdatei drei weitere Headerdateien im jeweiligen Include-Verzeichnis.
- patch an.
- Sind die Headerdateien aktualisiert, kompiliert er die notwendigen Bibliotheken mit dem jeweiligen Compiler.
Beispiel 1: Migration nach C++Builder 2009/Unicode
const unsigned majorVersion = 1, minorVersion = 2;
AnsiString theMessage = AnsiString ().sprintf ("Hello %s!\n"
"This machine is running since %d minutes. "
"High time for a coffee break!",
EdtUserName->Text.c_str (), GetTickCount () / 1000 / 60);
AnsiString theTitle = AnsiString ().sprintf (
"%s v%d.%2d Professional Edition",
Application->Title, majorVersion, minorVersion);
MessageBox (Handle, theMessage.c_str (), theTitle.c_str (),
MB_ICONINFORMATION);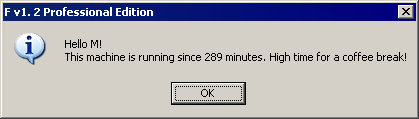
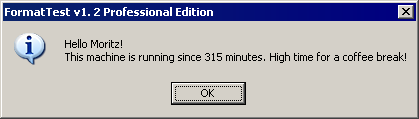
 SystemCppException wird die Fehlermeldung schon etwas informativer:
SystemCppException wird die Fehlermeldung schon etwas informativer: const_cast<>int und unsigned longAnsiString (EdtUserName->Text).c_str ()
const_cast<>int und unsigned longAnsiString (EdtUserName->Text).c_str () sprintf()String::c_str() eine wohldokumentierte Alternative existiert.
sprintf()String::c_str() eine wohldokumentierte Alternative existiert.Auch diesen Fehler beseitigen wir genau wie oben, und schon funktioniert alles:
Beispiel 2: Debuggen komplizierterer Format-Strings
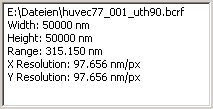
std::vector <String> values;
values.push_back (String ().sprintf (_D ("File path: %s"),
image->getImagePath ().c_str ()));
values.push_back (String ().sprintf (_D ("Width: %f %s"),
ppimage.getXLength (), ppimage.getXUnit ().c_str ()));
values.push_back (String ().sprintf (_D ("Height: %f %s"),
ppimage.getYLength (), ppimage.getYUnit ().c_str ()));
values.push_back (String ().sprintf (_D ("Range: %.3f %s"),
ppimage.getMaxVal () - ppimage.getMinVal (),
ppimage.getZUnit ().c_str ()));
values.push_back (String ().sprintf (_D ("X Resolution: %.3f %s/px"),
ppimage.getXLength () / ppimage.getWidth (),
ppimage.getXUnit ().c_str ()));
values.push_back (String ().sprintf (_D ("Y Resolution: %.3f %s/px"),
ppimage.getYLength () / ppimage.getHeight (),
ppimage.getYUnit ().c_str ()));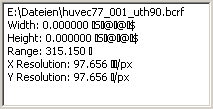
// format_error.hpp
namespace cbde
{
...
typedef void (*FormatStringErrorHandlerT) (const FormatStringErrorDescriptor& fse);
void setFormatStringErrorHandler (FormatStringErrorHandlerT newHandler);
FormatStringErrorHandlerT getFormatStringErrorHandler (void);
// This is the default.
void formatStringErrorException (const FormatStringErrorDescriptor& fse);
void formatStringErrorMessageAndAbort (const FormatStringErrorDescriptor& fse);
// Asks the user what to do next. Suitable for debugging purposes only.
void formatStringErrorDebug (const FormatStringErrorDescriptor& fse);
} // namespace cbde // Project.cpp
...
#include <cbde/format_error.hpp>
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
USEFORM("MainUnit.cpp", FrmMain);
...
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
WINAPI _tWinMain(HINSTANCE, HINSTANCE, LPTSTR, int)
{
try
{
cbde::setFormatStringErrorHandler (cbde::formatStringErrorDebug);
...
Lokalisierungen mit gettext haben unter anderem den Vorteil der einfachen Erweiterbarkeit: jeder Nutzer des Programmes kann poEditCBDE_FORMAT_CHECK_DEBUG (mit Positionsinformation, also Dateiname, Zeilennummer und Funktion) oder CBDE_FORMAT_CHECK (ohne Positionsinformation) aktiviert werden.
Aktiviert man CBDE_FORMAT_CHECK
; MainUnit.cpp.42: std::fprintf (stderr, gettext ("E2094: Operator '%s' is...
004019B4 8B4D10 mov ecx,[ebp+$10]
004019B7 51 push ecx
004019B8 8B450C mov eax,[ebp+$0c]
004019BB 50 push eax
004019BC 8B5508 mov edx,[ebp+$08]
004019BF 52 push edx
004019C0 68FA114700 push $004711fa
004019C5 E8BAFFFFFF call _gettext
004019CA 59 pop ecx
004019CB 50 push eax
004019CC 8B0DD0CD4700 mov ecx,[$0047cdd0]
004019D2 83C130 add ecx,$30
004019D5 51 push ecx
004019D6 E8ADF30600 call _fprintf
004019DB 83C414 add esp,$14Mit CBDE_FORMAT_CHECK wird folgendes generiert:
; MainUnit.cpp.42: std::fprintf (stderr, gettext ("E2094: Operator '%s' is...
004019B7 8B7510 mov esi,[ebp+$10]
004019BA 8B7D0C mov edi,[ebp+$0c]
004019BD 8B4508 mov eax,[ebp+$08]
004019C0 8945D4 mov [ebp-$2c],eax
004019C3 68FA214700 push $004721fa
004019C8 E8B7FFFFFF call _gettext
004019CD 8BD8 mov ebx,eax
004019CF A1D0DD4700 mov eax,[$0047ddd0]
004019D4 59 pop ecx
004019D5 83C030 add eax,$30
004019D8 8945D0 mov [ebp-$30],eax
004019DB 6A03 push $03
004019DD 68D0224700 push $004722d0
004019E2 53 push ebx
004019E3 E830280000 call cbde::verifyPrintfFormatString(const char *,...
004019E8 83C40C add esp,$0c
004019EB 56 push esi
004019EC 57 push edi
004019ED 8B55D4 mov edx,[ebp-$2c]
004019F0 52 push edx
004019F1 53 push ebx
004019F2 8B4DD0 mov ecx,[ebp-$30]
004019F5 51 push ecx
004019F6 E815F60600 call _fprintf
004019FB 83C414 add esp,$14 static const unsigned argTypeTable[3] = {
cbde::TypeID <decltype (op)>::value,
cbde::TypeID <decltype (lhstype)>::value,
cbde::TypeID <decltype (rhstype)>::value,
};
const char* theFormatString = gettext ("E2094: Operator '%s' is not "
"implemented in type '%s' "
"for arguments of type '%s'");
cbde::verifyPrintfFormatString (theFormatString, argTypeTable,
sizeof (argTypeTable) / sizeof (unsigned));
std::fprintf (stderr, theFormatString, op, lhstype, rhstype);str_printf()-Funktion zeigen:
object TFormatHeaderSettings: TPersistenceWrapper Persistent.MaxFormatParams = 12 Persistent.MaxFixedParams = 3 Persistent.FormatNames.Strings = ( 'str_printf' 'wstr_printf' 'printf' 'wprintf' 'sprintf' 'swprintf' 'fprintf' 'fwprintf' 'scanf' 'wscanf' 'sscanf' 'swscanf' 'fscanf' 'fwscanf' 'snprintf' 'snwprintf' '_snprintf' '_snwprintf' 'cat_printf' 'cat_sprintf') end- Sodann rufe man aus der Kommandozeile FORMATGEN defaultHeaderSettings.dat "$(BDS)\include\cbde" auf (und ersetze $(BDS) durch den Pfad der C++Builder-Installation).
#ifndef _STR_PRINTF_HPP #define _STR_PRINTF_HPP #include <string> + #include <cbde/format_definition_begin.hpp> std::string str_printf (const char* format, ...); + // Printf|Scanf, format_string_type, return_type, func_name + CBDE_FORMAT_DECLARE_SAFE (Printf, const char*, std::string, str_printf) + #include <cbde/format_definition_end.hpp> #endif // _STR_PRINTF_HPP
Referenzen
[1] Wikipedia: Format string vulnerabilities, zum Stand am 08.06.2009
[2] Boost Format library
[3] Using the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC): Options to Request or Suppress Warnings (-Wformat)
[4] Joel Spolsky: Back to Basics, 11.12.2001
Kommentare
Deprecated: mysql_connect(): The mysql extension is deprecated and will be removed in the future: use mysqli or PDO instead in /www/htdocs/w008ab83/ad/phputils/dbc_mysql.php on line 112